 Painted spiny lobster, Panulirus versicolor
Painted spiny lobster, Panulirus versicolorCrustaceans include crabs, lobsters, shrimps, barnacles, and similar animals. Crustaceans have two-parted limbs and a distinct larval phase. Most are free-living aquatic animals. Their bodes consist of three segments, the head, the thorax, and the abdomen. Crustaceans have hard exoskeletons which must be moulted for the animals to grow.
Lobsters have long bodies with muscular tails. They live in crevices or burrows in the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs have claws. Spiny lobsters are not closely related to clawed lobsters.
 Painted spiny lobster, Panulirus versicolor
Painted spiny lobster, Panulirus versicolor
Squat lobsters are flattened crustaceans with long tails held curled beneath the cephalothorax.

 Elegant crinoid squat lobster, Allogalathea elegans
Elegant crinoid squat lobster, Allogalathea elegans


 Tanegashima squat lobster, Galathea tanegashimae
Tanegashima squat lobster, Galathea tanegashimae
Crabs are decapod crustaceans which typically have a very short projecting tail which is usually hidden under the thorax. They have a thick exoskeleton and a single pair of pincers.
 Zebra urchin crab, Zebrida adamsii
Zebra urchin crab, Zebrida adamsii
 Haig's porcelain crab, Porcellanella haigae
Haig's porcelain crab, Porcellanella haigae
 Conical spider crab, Xenocarcinus conicus
Conical spider crab, Xenocarcinus conicus

 Soft coral porcelain crab, Lissoporcellana nakasonei
Soft coral porcelain crab, Lissoporcellana nakasonei
 Paleface coral crab, Tetralia cinctipes
Paleface coral crab, Tetralia cinctipes
 Red swimming crab, Charybdis paucidentata
Red swimming crab, Charybdis paucidentata
 Rainbow swimming crab, Charybdis cf erythrodactyla
Rainbow swimming crab, Charybdis cf erythrodactyla
 [unidentified swimming crab, Portunus sp.?]
[unidentified swimming crab, Portunus sp.?]
 Splendid red spooner crab, Etisus splendidus
Splendid red spooner crab, Etisus splendidus






 [unidentified decorator crabs]
[unidentified decorator crabs]
 Hydroid decorator crab, Hyastenus bispinosus
Hydroid decorator crab, Hyastenus bispinosus
 Corallimorph decorator crab, Cyclocoeloma tuberculata
Corallimorph decorator crab, Cyclocoeloma tuberculata
 Bull hydroid crab, Naxioides taurus
Bull hydroid crab, Naxioides taurus
 [unidentified swimming crab, Portunus sp.?]
[unidentified swimming crab, Portunus sp.?]

 [unidentified swimming crabs, Carupa sp.?]
[unidentified swimming crabs, Carupa sp.?]

 Red-dotted guard crab, Trapezia cymodoce
Red-dotted guard crab, Trapezia cymodoce
Shrimps are decapod crustaceans with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion. Shrimp have thin fragile legs that are used mostly for perching.
 Hinge-beak shrimp, Cinetorhynchus sp.
Hinge-beak shrimp, Cinetorhynchus sp.
 Purple urchin shrimp, Stegopontonia cf commensalis
Purple urchin shrimp, Stegopontonia cf commensalis
 Squat shrimp, Thor amboinensis
Squat shrimp, Thor amboinensis


 Holthuis's anemone shrimp, Ancylomenes holthuisi
Holthuis's anemone shrimp, Ancylomenes holthuisi
 Coleman shrimp, Periclimenes colemani
Coleman shrimp, Periclimenes colemani
 Magnificent anemone shrimp, Ancylomenes magnificus
Magnificent anemone shrimp, Ancylomenes magnificus


 Emperor shrimp, Periclimenes imperator
Emperor shrimp, Periclimenes imperator
 Banded coral shrimp, Stenopus hispidus
Banded coral shrimp, Stenopus hispidus

 Translucent gorgonium shrimp, Manipontonia psamathe
Translucent gorgonium shrimp, Manipontonia psamathe
Hermit crabs are decapod crustaceans with an asymmetrical, long, spirally curved, soft abdomen that is concealed in a scavenged mollusc shell carried around by the hermit crab, into which the whole body can retract.


 Anemone hermit crab, Dardanus pedunculatus
Anemone hermit crab, Dardanus pedunculatus
 Pale anemone hermit crab, Dardanus deformis
Pale anemone hermit crab, Dardanus deformis
 Tiny hermit crab, Pagurixus rubrovittatus
Tiny hermit crab, Pagurixus rubrovittatus
 Morgan's coral hermit crab, Paguritta morgani
Morgan's coral hermit crab, Paguritta morgani
Mantis shrimps (stomatopods) have powerful claws that are used to attack and kill prey by spearing, stunning, or dismembering. Their eyes are mounted on mobile stalks and can move independently of each other.

 Peacock mantis, Odontodactylus scyllarus
Peacock mantis, Odontodactylus scyllarus
Isopods have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennas, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under the thorax.
Amphipods have no carapace and have a laterally compressed body. Most are scavengers.
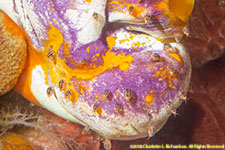 Dalmatian ladybug amphipods, Cyproideidae sp.
Dalmatian ladybug amphipods, Cyproideidae sp.
Skeleton shrimp are a kind of amphipod. They have slender threadlike bodies. The males are much larger than the females.
 Red-stripe keleton shrimp, Protella similis
Red-stripe keleton shrimp, Protella similis
Copepods have a larval form which has a head and tail but no thorax or abdomen. The larva, called a nauplius, is so different from the adult that they were once thought to be a different species. About half of the known copepod species are parasitic.
©2019, 2024 Mermaid Underwater Photographic. All Rights Reserved.
Contact us at mermaid@underwater.org.
Last modified 30 October 2024