 Pink anemonefish, Amphiprion perideraion
Pink anemonefish, Amphiprion perideraionMore than three thousand species of fish are found within the "coral triangle".
NOTE: We are not experts on these animals. If we have misidentified one, or if you can identify one we could not identify, please email us so we can correct it.
Anemonefish or clownfish form symbiotic mutualisms with sea anemones. Most are orange, yellow, red, or black, often with white stripes. They are omnivorous and can feed on leftover food from their host anemone. Fecal matter from the fish provides nutrients to the anemone.,
 Pink anemonefish, Amphiprion perideraion
Pink anemonefish, Amphiprion perideraion



 Clark's anemonefish, Amphiprion clarkii
Clark's anemonefish, Amphiprion clarkii
 False clown anemonefish, Amphiprion ocellaris
False clown anemonefish, Amphiprion ocellaris
 Tomato anemonefish, Amphiprion frenatus
Tomato anemonefish, Amphiprion frenatus
Angelfish have deep, laterlally compressed bodies. They resemble butterflyfish but have strong preopercle spines on the gill covers. Many species have streamer-like extensions of the soft dorsal and anal fins.
 Regal angelfish, Pygoplites diacanthus
Regal angelfish, Pygoplites diacanthus
 Blue-girdled angelfish, Pomacanthus navarchus
Blue-girdled angelfish, Pomacanthus navarchus
 Semicircle angelfish, Pomacanthus semicirculatus
Semicircle angelfish, Pomacanthus semicirculatus
 Emperor angelfish, Pomacanthus imperator
Emperor angelfish, Pomacanthus imperator

 Three-spot angelfish, Apolemichthys trimaculata
Three-spot angelfish, Apolemichthys trimaculata
 Six-banded angelfish, Pomacanthus sexstriatus
Six-banded angelfish, Pomacanthus sexstriatus
Anthias are mainly pink, orange, or yellow. They form large shoals. Within the shoal, harems consist of one dominanat, colorful male, two to twelve females, and up to two subdominanat males. All anthias are born female. If a dominant male dies, the largest female will develop into a male and take its place.



 Scalefin anthias, Pseudanthias squamipinnis
Scalefin anthias, Pseudanthias squamipinnis
Bannerfish look like smaller versions of angelfish, but lack preopercle spines on their gill covers.
 Humphead bannerfish, Heniochus varius
Humphead bannerfish, Heniochus varius
 Singular bannerfish, Heniochus singularius
Singular bannerfish, Heniochus singularius
 Schooling bannerfish, Heniochus diphreutes
Schooling bannerfish, Heniochus diphreutes
 Long-fin bannerfish, Heniochus acuminatus
Long-fin bannerfish, Heniochus acuminatus
Blennies are small fish with elongated bodies and relatively large eyes and mouths. They spend much of their time on or near the sea floor.
 Striped fangblenny, Meiacanthus granunistes
Striped fangblenny, Meiacanthus granunistes


 Bath's blenny (color variants), Ecsenius bathi
Bath's blenny (color variants), Ecsenius bathi
 Miracle triplefin, Enneapterygius mirabilis
Miracle triplefin, Enneapterygius mirabilis
Boxfishes are square bony fishes related to pufferfish and filefish.

 Yellow boxfish (juvenile, right), Ostracion cubicus
Yellow boxfish (juvenile, right), Ostracion cubicus

 Humpback turretfish, Tetrosomus gibbosus
Humpback turretfish, Tetrosomus gibbosus
Butterflyfish look like smaller versions of angelfish but lack preopercle spines on their gill covers.
 Speckled butterflyfish, Chaetodon citrinellas
Speckled butterflyfish, Chaetodon citrinellas
 Threadfin butterflyfish, Chaetodon auriga
Threadfin butterflyfish, Chaetodon auriga
 Redfin butterflyfish, Chaetodon lunulatus
Redfin butterflyfish, Chaetodon lunulatus
 Spot-tail butterflyfish, Chaetodon ocellicaudus
Spot-tail butterflyfish, Chaetodon ocellicaudus
 Black-backed butterflyfish, Chaetodon melannotus
Black-backed butterflyfish, Chaetodon melannotus
 Meyer's butterflyfish, Chaetodon meyeri
Meyer's butterflyfish, Chaetodon meyeri
 Oval-spot butterflyfish, Chaetodon speculum
Oval-spot butterflyfish, Chaetodon speculum
 Orange-banded coralfish, Coradion chrysozonus
Orange-banded coralfish, Coradion chrysozonus
 Raccoon butterflyfish, Chaetodon lunula
Raccoon butterflyfish, Chaetodon lunula
 Longnose butterflyfish, Forcipiger longirostris
Longnose butterflyfish, Forcipiger longirostris
 Klein's butterflyfish, Chaetodon kleinii
Klein's butterflyfish, Chaetodon kleinii
 Saddled butterflyfish, Chaetodon ephippium
Saddled butterflyfish, Chaetodon ephippium
 Vagabond butterflyfish, Chaetodon vagabundus
Vagabond butterflyfish, Chaetodon vagabundus
 Chevroned butterflyfish, Chaetodon trifascialis
Chevroned butterflyfish, Chaetodon trifascialis
 Lined butterflyfish, Chaetodon lineolatus
Lined butterflyfish, Chaetodon lineolatus
Cardinalfish are primarily marine ray-finned fish. They are generally small and often brightly colored. They have large mouths and their dorsal fins are divided into two seprate fins. They are mainly nocturnal.
 Orange-spot cardinalfish, Apogon rubrimacula
Orange-spot cardinalfish, Apogon rubrimacula
 Spur-cheek cardinalfish, Apogon fraenatus
Spur-cheek cardinalfish, Apogon fraenatus
 Black-nosed cardinalfish, Apogon cf. cypselurus
Black-nosed cardinalfish, Apogon cf. cypselurus
 Blackstripe cardinalfish, Apogon nigrofasciatus
Blackstripe cardinalfish, Apogon nigrofasciatus
 Wassinki cardinalfish, Apogon wassinki
Wassinki cardinalfish, Apogon wassinki
 Toothy cardinalfish, Cheilodipterus isostigmus
Toothy cardinalfish, Cheilodipterus isostigmus

 Frostfin cardinalfish, Apogon cf. hoevenii
Frostfin cardinalfish, Apogon cf. hoevenii
 Spotnape cardinalfish, Apogon notatus
Spotnape cardinalfish, Apogon notatus
Catfish have fused second dorsal, caudal, and anal fins like eels. The mouth is surrounded by four pairs of barbels. The first dorsal and each of the pectoral fins have a highly venomous spine.
 Striped catfish, Plotosus lineatus
Striped catfish, Plotosus lineatus
Coral breams are benthic carnivores.
 Striped monocle bream, Scolopsis lineatus
Striped monocle bream, Scolopsis lineatus
 Bridled monocle bream, Scolopsis bilineatus
Bridled monocle bream, Scolopsis bilineatus
 Humpnose bigeye bream, Monotaxis grandoculis
Humpnose bigeye bream, Monotaxis grandoculis
 Striped large-eye bream, Gnathodentex aureolineatus
Striped large-eye bream, Gnathodentex aureolineatus
Cornetfish are extremely elongated fish found in tropical and subtropical marine environments worldwide. They have very long snouts, distinct dorsal and anal fins, and forked caudal fins whose center rays form a lengthy filament.


 Cornetfish, Fistularia commersonii
Cornetfish, Fistularia commersonii
Damselfish have bright colors or strongly contrasting patterns.
 Golden damsel, Amblyglyphidodon aureus
Golden damsel, Amblyglyphidodon aureus
 Blackbar chromis, Chromis retrofasciata
Blackbar chromis, Chromis retrofasciata
 Reticulated dascyllus, Dascyllus reticulatus
Reticulated dascyllus, Dascyllus reticulatus
 Blue-green chromis, Chromis viridis
Blue-green chromis, Chromis viridis

 Philippines chromis, Chromis scotochiloptera
Philippines chromis, Chromis scotochiloptera
 Indo-Pacific sargeant, Abudefduf vaigiensis
Indo-Pacific sargeant, Abudefduf vaigiensis
 Black damsel, Neoglyphidodon melas
Black damsel, Neoglyphidodon melas
 Yellow chromis, Chromis analis
Yellow chromis, Chromis analis
 Ternate chromis, Chromis ternatensis
Ternate chromis, Chromis ternatensis
 Kuiter's demoiselle, Chrysiptera kuiteri
Kuiter's demoiselle, Chrysiptera kuiteri
 Black-banded demoiselle, Amblypomacentrus breviceps
Black-banded demoiselle, Amblypomacentrus breviceps
 Komodo damsel, Pomacentrus komodoensis
Komodo damsel, Pomacentrus komodoensis
 Bicolor chromis, Chromis margaritifer
Bicolor chromis, Chromis margaritifer


 Three-spot dascyllus (adults left two images, juveniles right), Dascyllus trimaculatus
Three-spot dascyllus (adults left two images, juveniles right), Dascyllus trimaculatus
 Ambon chromis, Chromis amboinensis
Ambon chromis, Chromis amboinensis
Dartfish are goby-like fish.
 Fire dartfish, Nemateleotris magnifica
Fire dartfish, Nemateleotris magnifica
Eels: in moray eels, the dorsal fin extends from just behind the head along the back and joins seamlessly with the caudal and anal fins. Morays have rather small eyes, relying on their sense of smell to ambsh prey. Garden eels are conger eels. These small eels live in burrows in the sea floor


 Yellowmargin moray, Gymnothorax flavimarginatus
Yellowmargin moray, Gymnothorax flavimarginatus
 White-eyed moray, Siderea thysoidea
White-eyed moray, Siderea thysoidea
 Giant moray, Gymnothorax javanicus
Giant moray, Gymnothorax javanicus
 Unicolor moray, Echidna unicolor
Unicolor moray, Echidna unicolor
 Minor moray, Gymnothorax cf. minor
Minor moray, Gymnothorax cf. minor
 Spotted garden eels, Heteroconger hassi
Spotted garden eels, Heteroconger hassi
Flatheads have wide flattened bodies. Both eyes are on top of the flattened head. They can change ciolor and hide in the sand.

 Horned flathead, Thysanophrys carbunculus
Horned flathead, Thysanophrys carbunculus
Flounders are several species of flatfish which are only distantly related to each other. As a flounder matures, one eye migrates to the other side of the animal's head.
 Peacock sole, Pardachirus cf. pavoninus
Peacock sole, Pardachirus cf. pavoninus

 Leopard flounder, Bothus pantherinus
Leopard flounder, Bothus pantherinus
 Peacock flounder, Bothus mancus
Peacock flounder, Bothus mancus
Frogfish are small, short, stocky anglerfish, often covered in spinnules and other camouflage. Many species can change color.

 Giant frogfish, Antennarius commersoni
Giant frogfish, Antennarius commersoni
 Painted frogfish, Antennarius pictus
Painted frogfish, Antennarius pictus
Fusiliers are related to snappers, but are adapted for feeding on plankton rather than larger prey. Theuy are cylindrical, streamlined fishes.
 Lunar fusilier, Caesio lunaris
Lunar fusilier, Caesio lunaris

 Scissortail fusilier, Caesio caerulaurea
Scissortail fusilier, Caesio caerulaurea

 Bluestreak fusilier (two color phases), Pterocaesio tile
Bluestreak fusilier (two color phases), Pterocaesio tile
 Twinstripe fusilier, Pterocaesio marri
Twinstripe fusilier, Pterocaesio marri
 Narrow-stripe fusilier, Pterocaesio tessellata
Narrow-stripe fusilier, Pterocaesio tessellata
 Yellowback fusilier, Caesio xanthonota
Yellowback fusilier, Caesio xanthonota
Goatfish have a pair of chin barbels used to probe the sand for food. Many are brightly colored.
 Yellowstripe goatfish (night colors), Mulloidichthys flavolineatus
Yellowstripe goatfish (night colors), Mulloidichthys flavolineatus
 Longbarbel goatfish, Parupeneus macronemua
Longbarbel goatfish, Parupeneus macronemua
 Freckled goatfish, Upeneus tragula
Freckled goatfish, Upeneus tragula
 Island goatfish, Parupeneus insularis
Island goatfish, Parupeneus insularis
 Yellowfin goatfish, Mulloidichthys vanicolemsis
Yellowfin goatfish, Mulloidichthys vanicolemsis
Gobies form one of the largest fish families. Most are bottom-dwellers.
 Orange-dashed goby, Valenciennes puellaris
Orange-dashed goby, Valenciennes puellaris
 Signal-fin goby, Coryphopterus signipinnis
Signal-fin goby, Coryphopterus signipinnis
 Randall's shrimpgoby, Amblyeleotris randalli
Randall's shrimpgoby, Amblyeleotris randalli
 Yellow and white striped pygmygoby, Eviota mikiae
Yellow and white striped pygmygoby, Eviota mikiae

 Steinitz' shrimpgoby, Amblyeleotris steinitzi
Steinitz' shrimpgoby, Amblyeleotris steinitzi
 White-striped pygmygoby, Eviota guttata
White-striped pygmygoby, Eviota guttata

 Signal goby, Signigobius biocellatus
Signal goby, Signigobius biocellatus
 Silverspot shrimpgoby, Ctenogobiops crocineus
Silverspot shrimpgoby, Ctenogobiops crocineus
Groupers have stout bodies and large mouths. They swallow their prey whole rather than biting off pieces. They have heavy crushing tooth plates.
 Snubnose grouper, Epinephelus macrospilos
Snubnose grouper, Epinephelus macrospilos
 Leopard grouper, Cephalopholis leopardus
Leopard grouper, Cephalopholis leopardus
 Coral grouper, Cephalopholis miniata
Coral grouper, Cephalopholis miniata

 Slender grouper, Anyperodon cf. leucogrammicus
Slender grouper, Anyperodon cf. leucogrammicus
 Saddle grouper, Cephalopholis sexmaculata
Saddle grouper, Cephalopholis sexmaculata
 Blacksaddle grouper, Epinephalus howlandi
Blacksaddle grouper, Epinephalus howlandi
Gurnards have greatly enlarged pectoral fins. They can walk along sandy bottoms using their peectoral fins.

 Helmut gurnard, Dactyloptena orientalis
Helmut gurnard, Dactyloptena orientalis
Hawkfish have large heads with thick, elongated bodies. Their dorsal fins are merged. At the tip of each spine are several trailing filaments.

 Freckled hawkfish, Paracirrhites forsteri
Freckled hawkfish, Paracirrhites forsteri

 Pixy hawkfish, Cirrhitichthys oxycephalus
Pixy hawkfish, Cirrhitichthys oxycephalus
 Threadfin hawkfish, Cirrhitichthys aprinus
Threadfin hawkfish, Cirrhitichthys aprinus
Lionfish have conspicuous warning coloration and venomous spiky fin rays. There are twelve species.


 Common lionfish, Pterois volitans
Common lionfish, Pterois volitans
 Kodipungi lionfish, Pterois cf. kodipungi
Kodipungi lionfish, Pterois cf. kodipungi
 Shortfin lionfish, Dendrochirus brachypterus
Shortfin lionfish, Dendrochirus brachypterus
 Spotfin lionfish, Pterois antennata
Spotfin lionfish, Pterois antennata
Lizardfish are bottom-dwelling marine fish. They have slender somewhat cylindrical bodies. Their heads superficially resemble those of lizards.

 Reef lizardfish, Synodus variegatus
Reef lizardfish, Synodus variegatus
 Blackblotch lizardfish, Synodus jaculum
Blackblotch lizardfish, Synodus jaculum
The Moorish idol is the only member of its family.
Parrotfish have teeth forming a tightly-packed mosaic on the external surface of their jaw bones, forming a parrot-like beak used to rasp algae off of coral.
 Greenthroat parrotfish, Scarus prasiognathos
Greenthroat parrotfish, Scarus prasiognathos

 Redlip parrotfish, Scarus rubroviolaceus
Redlip parrotfish, Scarus rubroviolaceus
 Bower's parrotfish, Chlorurus bowersi
Bower's parrotfish, Chlorurus bowersi


 Bridled parrotfish, Scarus frenatus
Bridled parrotfish, Scarus frenatus


 Bicolor parrotfish, Cetoscarus bicolor
Bicolor parrotfish, Cetoscarus bicolor
 Bumphead parrotfish, Bolbometopon muricatum
Bumphead parrotfish, Bolbometopon muricatum
Pipefish look like straight-bodied sea horses with tiny mouths. They have a highly-modified skeleton formed into armored plating. Ghost pipefishes are related to pipefishes and seahorses. They usually float mouth downards near a background which makes them hard to see. Female ghost pipefish use their enlarged pelvic fins to brood their eggs until they hatch.

 Ornate ghost pipefish, Solenostomus paradoxus
Ornate ghost pipefish, Solenostomus paradoxus
 Robust ghost pipefish, Solenostomus cyanopterus
Robust ghost pipefish, Solenostomus cyanopterus
 Ringed pipefish, Dunckerocampus dactyliophorus
Ringed pipefish, Dunckerocampus dactyliophorus
Puffers are mostly toxic, including some of the most poisonous vertebrates in the world. A puffer can fill its extremely elastic stomach with water or even air until it is much larger and nearly spherical. All puffers have spines, not always visible unless the fish is inflated.



 Black-spotted puffer, Arothron nigropunctatus
Black-spotted puffer, Arothron nigropunctatus
 Striped puffer, Arothron manilensis
Striped puffer, Arothron manilensis
 Black-saddled toby, Canthigaster valentini
Black-saddled toby, Canthigaster valentini
 Fingerprint toby, Canthigaster compressa
Fingerprint toby, Canthigaster compressa
 Star puffer, Arothron stellatus
Star puffer, Arothron stellatus
Rabbitfish are native to shallow Indo-Pacfic waters. They are commercially important food fish.
 Foxface rabbitfish, Siganus vulpinus
Foxface rabbitfish, Siganus vulpinus
 Masked rabbitfish, Siganus puellus
Masked rabbitfish, Siganus puellus
Rays are the largest group of cartilaginous fish and are closely related to sharks. Rays have flattened bodies, enlarged pectoral fins that are fused to the head, and gill slits on their ventral surface.
 Blue-spotted ribbontail ray, Taeniura hymma
Blue-spotted ribbontail ray, Taeniura hymma
 Cowtail stingray, Pastinachus sephen
Cowtail stingray, Pastinachus sephen
 Spotted eagle ray, Aetobatus narinari
Spotted eagle ray, Aetobatus narinari
In remoras the first dorsal fin takes the form of a modified oval, sucker-like organ with slat-like structures that open and close to create suction. By sliding backward the remora can increase suction. It can release itself by swimming forward.
 Sharksucker, Echeneis naucrates
Sharksucker, Echeneis naucrates
Sandperches are benthic fish which normally live on sand or rubble substrates. They have elongated bodies which are flattened posteriorly and cylindrical towards the head. They tend to sit on the sea bed, their bodies propped up by the widely separated pelvic fins.
 Reticulated sandperch, Parapercis tetracantha
Reticulated sandperch, Parapercis tetracantha
 Speckled sandperch, Parapercis hexophthalma
Speckled sandperch, Parapercis hexophthalma

 Blackfin sandperch, Parapercis snyderi
Blackfin sandperch, Parapercis snyderi
 Nosestripe sandperch, Parapercis lineopunctata
Nosestripe sandperch, Parapercis lineopunctata
 Yellowtail sandperch, Parapercis sp.
Yellowtail sandperch, Parapercis sp.
 Spotted sandperch, Parapercis millipunctata
Spotted sandperch, Parapercis millipunctata
Scorpionfish include many of the world's most venomous species. They have sharp spines coated with venomous mucus.

 Poss's scorpionfish, Scorpaenopsis possi
Poss's scorpionfish, Scorpaenopsis possi
 Papuan scorpionfish, Scorpaenopsis papuensis
Papuan scorpionfish, Scorpaenopsis papuensis
 Raggy scorpionfish, Scorpaenopsis venosa
Raggy scorpionfish, Scorpaenopsis venosa
 Caledonian devilfish, Inimicus caledonicus
Caledonian devilfish, Inimicus caledonicus
 Spiny devilfish, Inimicus didactylus
Spiny devilfish, Inimicus didactylus

 Leaf scorpionfish, Taenianotus triacanthus
Leaf scorpionfish, Taenianotus triacanthus
Sharks are elasmobranch fish with a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the side of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head.


 Gray reef shark, Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos
Gray reef shark, Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos



 Whitetip reef shark, Triaenodon obesus
Whitetip reef shark, Triaenodon obesus
 Tawny nurse shark, Nebrius ferrugineus
Tawny nurse shark, Nebrius ferrugineus
Snappers are active carnivores which feed on crustaceans or smaller fish.
 Midnight snapper, Macolor macularis
Midnight snapper, Macolor macularis
 Golden-lined snapper, Lutjanus rufolineatus
Golden-lined snapper, Lutjanus rufolineatus
 Bluestripe snapper, Lutjanus kasmira
Bluestripe snapper, Lutjanus kasmira
Soldierfish are ray-finned fish with relatively large eyes. In some species the preopercle spines are venomous.
 Splendid soldierfish, Myripristis botche
Splendid soldierfish, Myripristis botche


 Crescent-tail bigeye, Priacanthus hamrur
Crescent-tail bigeye, Priacanthus hamrur
 Tailspot soldierfish, Sargocentron caudimaculatum
Tailspot soldierfish, Sargocentron caudimaculatum
 Blotcheye soldierfish, Myripristis murdjan
Blotcheye soldierfish, Myripristis murdjan
Spadefish are spade-shaped and laterally compressed and have very symmetrical triangular dorsal and anal fins.
 Golden spadefish, Platax boersii
Golden spadefish, Platax boersii
Surgeonfish have one or more scalpel-like spines on either side of the tail.
 Brown surgeonfish, Acanthurus nigrofuscus
Brown surgeonfish, Acanthurus nigrofuscus
 Mimic surgeonfish, Acanthurus pyroferus
Mimic surgeonfish, Acanthurus pyroferus
 Indian mimic surgeonfish, Acanthurus tristis
Indian mimic surgeonfish, Acanthurus tristis
 Lined bristletooth, Ctenochaetus striatus
Lined bristletooth, Ctenochaetus striatus


 Yellowmask surgeonfish, Acanthurus mata
Yellowmask surgeonfish, Acanthurus mata
 Striped surgeonfish, Acanthurus lineatus
Striped surgeonfish, Acanthurus lineatus
 Blue-lipped bristletooth, Ctenochaetus cyanocheilus
Blue-lipped bristletooth, Ctenochaetus cyanocheilus
 White-cheek surgeonfish, Acanthurus nigricanis
White-cheek surgeonfish, Acanthurus nigricanis
 Fine-lined surgeonfish, Acanthurus grammoptilus
Fine-lined surgeonfish, Acanthurus grammoptilus
Sweetlips have big fleshy lips. They are usually seen in clusters under overhangs. Their colorings and patterning changes as the fish mature.
 Giant sweetlips, Plectorhinchus albovittatus
Giant sweetlips, Plectorhinchus albovittatus
 Ribbon sweetlips, Plectorhinchus polytaenia
Ribbon sweetlips, Plectorhinchus polytaenia

 Many-spotted sweetlips (juvenile, right), Plectorhinchus chaetodonoides
Many-spotted sweetlips (juvenile, right), Plectorhinchus chaetodonoides
 Somber sweetlips, Plectorhinchus unicolor
Somber sweetlips, Plectorhinchus unicolor


 Striped sweetlips (juvenile. right two images), Plectorhinchus lessonii
Striped sweetlips (juvenile. right two images), Plectorhinchus lessonii

 Oriental sweetlips (sub-adult, right), Plectorhinchus vittatus
Oriental sweetlips (sub-adult, right), Plectorhinchus vittatus
 Diagonal-banded sweetlips, Plectorhinchus lineatus
Diagonal-banded sweetlips, Plectorhinchus lineatus
 Harlequin sweetlips, Plectorhinchus chaetodonoides
Harlequin sweetlips, Plectorhinchus chaetodonoides
Triggerfish have an oval-shaped highly compressed body. They have large heads with small but strong-jawed mouths adapted for crushing shells. The eyes are small, set far back from the mouth, at the top of the head. The anterior dorsal fin is reduced to a set of three spines. The furst spine is stout and by far the longest. All three are normally retracted into a groove. Triggerfish can erect the first two dorsal spines, the first spine being locked in place by the erection of the short second spine, and can only be unlocked by depressing the second "trigger" spine.
 Blue triggerfish, Pseudobalistes fuscus
Blue triggerfish, Pseudobalistes fuscus
 Yellowmargin triggerfish, Pseudobalistes flavimarginatus
Yellowmargin triggerfish, Pseudobalistes flavimarginatus
 Titan triggerfish, Balistoides viridescens
Titan triggerfish, Balistoides viridescens
 Redtooth triggerfish, Odonus niger
Redtooth triggerfish, Odonus niger
 Orange-lined triggerfish, Balistapus undulatus
Orange-lined triggerfish, Balistapus undulatus
 Starry triggerfish, Abalistes stellatus
Starry triggerfish, Abalistes stellatus
 Clown triggerfish, Balistoides conspicillum
Clown triggerfish, Balistoides conspicillum
 Scythe triggerfish, Sufflamen bursa
Scythe triggerfish, Sufflamen bursa
Unicornfish are surgeonfish. Some species have a hornlike forehead extension.

 Bluetail unicornfish, Naso caeruleacauda
Bluetail unicornfish, Naso caeruleacauda
 Bignose unicornfish, Naso viamingii
Bignose unicornfish, Naso viamingii
Wrasses make up a diverse family of brightly-colored fish. Many wrasses have protractile mouths with separate jaw teeth the jut outwards. Many species have thick lips.
 Humphead wrasse, Cheilinus undulatus
Humphead wrasse, Cheilinus undulatus
 Tripletail wrasse, Cheilinus trilobatus
Tripletail wrasse, Cheilinus trilobatus

 Floral wrasse, Cheilinus chlorourus
Floral wrasse, Cheilinus chlorourus
 Linedcheek wrasse, Oxycheilinus digrammus
Linedcheek wrasse, Oxycheilinus digrammus
 Axilspot wrasse, Halichoeres podostigma
Axilspot wrasse, Halichoeres podostigma
 Bluespotted wrasse, Anampses caeruleopunctatus
Bluespotted wrasse, Anampses caeruleopunctatus
 Redbreasted wrasse, Cheilinus fasciatus
Redbreasted wrasse, Cheilinus fasciatus

 Cheeklined wrasse (female left, juvenile right), Oxycheilinus digramma
Cheeklined wrasse (female left, juvenile right), Oxycheilinus digramma
 Twospot wrasse (female), Oxycheilinus bimaculatus
Twospot wrasse (female), Oxycheilinus bimaculatus
 Cryptic wrasse, Pterogogus cryptus
Cryptic wrasse, Pterogogus cryptus
 Celebes wrasse, Oxycheilinus celebicus
Celebes wrasse, Oxycheilinus celebicus
 Red-eye wrasse, Cirrhilabrus solorensis
Red-eye wrasse, Cirrhilabrus solorensis
 Diana's hogfish, Bodianus diana
Diana's hogfish, Bodianus diana

 Crescent (moon) wrasse (adult left, juvenile right), Thalassoma lunare
Crescent (moon) wrasse (adult left, juvenile right), Thalassoma lunare

 Bluestreak cleaner wrasse (juvenile, right), Labroides dimidiatus
Bluestreak cleaner wrasse (juvenile, right), Labroides dimidiatus
 Jansen's wrasse, Thalassoma jansenii
Jansen's wrasse, Thalassoma jansenii
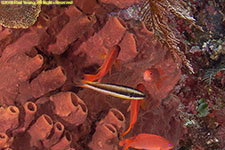 Yellowtail tubelip, Diproctacanthus xanthurus
Yellowtail tubelip, Diproctacanthus xanthurus
Others
 Urchin clingfish, Diademichthys lineatus
Urchin clingfish, Diademichthys lineatus
 Orange-striped emperor, Lethrinus obsoletus
Orange-striped emperor, Lethrinus obsoletus
 Bluefin trevally, Caranx melanpygus
Bluefin trevally, Caranx melanpygus
 Mackerel scad, Decapterus macarellus
Mackerel scad, Decapterus macarellus
©2019, 2020, 2024 Mermaid Underwater Photographic. All Rights Reserved.
Contact us at mermaid@underwater.org.
Last modified 30 October 2024